View the original Github Repo:
Naive Bayes is a popular rstatistical technique for e-mail filtering. It uses bag-of-words features (use countvectorizer to create the features from the text) to identify the email spam.
It uses a Bayes’ theorem to calculate a probability that an email is spam or not and it usually has low false positive spam detection rates, meaning that it rarely misclassify an legitimate email as spam. However, as its name suggest, it assumes strong and naive assumption about the independence of the words, which is rarely the case for words in the context.
Click here
Import the library
import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import seaborn as sns
%matplotlib inline
Explore the datasets
The datasets has been collected for SMS Spam research and it has two columns. One columns has the text and another shows the label(ham or spam)
spam_df = pd.read_csv("emails.csv")
spam_df.head()
| text | spam | |
|---|---|---|
| 0 | Subject: naturally irresistible your corporate... | 1 |
| 1 | Subject: the stock trading gunslinger fanny i... | 1 |
| 2 | Subject: unbelievable new homes made easy im ... | 1 |
| 3 | Subject: 4 color printing special request add... | 1 |
| 4 | Subject: do not have money , get software cds ... | 1 |
spam_df.tail()
| text | spam | |
|---|---|---|
| 5723 | Subject: re : research and development charges... | 0 |
| 5724 | Subject: re : receipts from visit jim , than... | 0 |
| 5725 | Subject: re : enron case study update wow ! a... | 0 |
| 5726 | Subject: re : interest david , please , call... | 0 |
| 5727 | Subject: news : aurora 5 . 2 update aurora ve... | 0 |
spam_df.describe()
| spam | |
|---|---|
| count | 5728.000000 |
| mean | 0.238827 |
| std | 0.426404 |
| min | 0.000000 |
| 25% | 0.000000 |
| 50% | 0.000000 |
| 75% | 0.000000 |
| max | 1.000000 |
spam_df.info()
<class 'pandas.core.frame.DataFrame'>
RangeIndex: 5728 entries, 0 to 5727
Data columns (total 2 columns):
# Column Non-Null Count Dtype
--- ------ -------------- -----
0 text 5728 non-null object
1 spam 5728 non-null int64
dtypes: int64(1), object(1)
memory usage: 89.6+ KB
spam_df["spam"].value_counts(normalize=True)
0 0.761173
1 0.238827
Name: spam, dtype: float64
Visualize the datasets
spam_df["length"] = spam_df["text"].apply(len)
spam_df.head()
| text | spam | length | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | Subject: naturally irresistible your corporate... | 1 | 1484 |
| 1 | Subject: the stock trading gunslinger fanny i... | 1 | 598 |
| 2 | Subject: unbelievable new homes made easy im ... | 1 | 448 |
| 3 | Subject: 4 color printing special request add... | 1 | 500 |
| 4 | Subject: do not have money , get software cds ... | 1 | 235 |
spam_df["length"].plot(bins=100, kind="hist")
<AxesSubplot:ylabel='Frequency'>
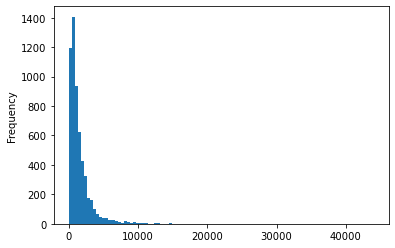
spam_df.length.describe()
count 5728.000000
mean 1556.768680
std 2042.649812
min 13.000000
25% 508.750000
50% 979.000000
75% 1894.250000
max 43952.000000
Name: length, dtype: float64
Clean the datasets
#remove punctutation
import string
#remove stopwords
from nltk.corpus import stopwords
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(spam_df["text"], spam_df["spam"], test_size=0.2)
def clean_message(message):
message = [char for char in message if char not in string.punctuation]
message = "".join(message)
message = [word for word in message.split() if word.lower() not in stopwords.words("english")]
message = " ".join(message)
return message
from sklearn.feature_extraction.text import CountVectorizer
CV = CountVectorizer()#min_df=0.01, max_features=300, stop_words="english")
CV.fit(X_train.apply(clean_message))
CountVectorizer()
X_train = CV.transform(X_train)
X_test = CV.transform(X_test)
Training the models
from sklearn.naive_bayes import MultinomialNB
NB_classifier = MultinomialNB()
NB_classifier.fit(X_train, y_train)
MultinomialNB()
Evaluate the model
from sklearn.metrics import classification_report, confusion_matrix
#predict the training set
y_predict_train = NB_classifier.predict(X_train)
cm = confusion_matrix(y_train, y_predict_train)
sns.heatmap(cm, annot=True)
<AxesSubplot:>

#predict the test set
y_predict_test = NB_classifier.predict(X_test)
cm = confusion_matrix(y_test, y_predict_test)
sns.heatmap(cm, annot=True)
<AxesSubplot:>
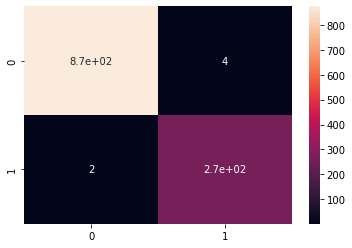
print(classification_report(y_test, y_predict_test))
precision recall f1-score support
0 1.00 1.00 1.00 878
1 0.99 0.99 0.99 268
accuracy 0.99 1146
macro avg 0.99 0.99 0.99 1146
weighted avg 0.99 0.99 0.99 1146